
ABACUS
Small and Handy
but a remarkably efficient Chinese Calculator
The Abacus, a sort of rectangular board with many
beads -- somewhat similar to what children use at
primary school to learn counting. Similar calculators
(1)
exist in several other countries, including Russia as
well as Japan, but with differentiating variations.
There is no doubt that it is one of the most
prominent articles of business equipment in Chinese
business offices today.
There is not a home or office in Taiwan where an
Abacus is not found. Its use is compulsory in all
primary and business schools. Of late, many a
foreigner is becoming interested in the use of the
(2)
Abacus in a increased number.
Wherever a Chinese goes, be it New York, London,
Bombay, Sidney or Buenos Aires, the Abacus goes
with him. Chinese government officials, bankers,
financiers, office clerks, junk dealers, and house wives
depend largely upon it for their counting in the same
manner, as a child depends on his mother. A Chinese
is so dependent on the Abacus that he finds it
awkward to make even simple calculations without one.
(3)
Naturally a great many expressions utilizing the
name of Abacus has developed out of this national
habit.
Today, there are more than 100 different models
of the Chinese Abacus varied in size and quality
of the materials used, but only one type made of brass
mounting on a marble base is the best.
This Chinese dependence on the Abacus is under-
(4)
standable in the light of what this simple gadget
can accomplish in the efficient calculations from
the simplest to the most complex mathematical
problems of addition, subtraction, multiplication and
division.
More briefly explained, the Abacus is an instrument
to augment mental arithmetic. The mechanics of its
use is simple, and its accuracy is assured by repetition
and practice alone.
(5)
Many speed and accuracy contests have been
staged between the Abacus and Calculating Machines.
The small, insignificant and inexpensive Abacus has
usually been the victor. It must be understood, how-
ever, that while the Abacus outshines its mechanical
brother in addition and subtraction, it faces some
disadvantages in multiplication and division problems.
(6)
INTRODUCTION TO "ABACUS"
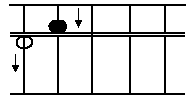
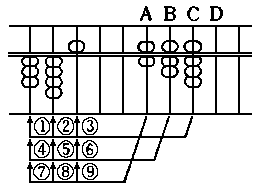
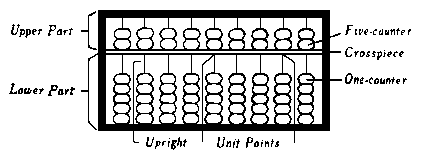 Unit points on the crosspiece are usually placed
(7)
Unit points on the crosspiece are usually placed
(7)
one every fifth upright.
Unit points are use to indicate "ones", "thousands",
"millions", "billions" and so on.
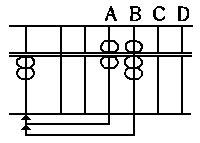
- How to manipulate your fingers.
In pushing the counters, there are three ways.
1) Use only the forefinger.
2) Using the thumb and forefinger.
3) Using the thumb, forefinger and middle finger.
(8)
The third one is the method with the thumb.
Of these three ways, the second one using the
thumb and forefinger is recommended, it being the
best and easiest.
Thumb used to: "Put in" counters in the lower part.
Forefinger used to: "Take off" the counters in the
lower part.
"Put in" a counter in the upper part.
(9)
"Take off" a counter in the upper part.
Note: "Put in" means pushing the counters toward
the crosspiece.
"Take off" means pushing the counters away
from the crosspiece.
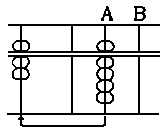
- How to manipulate counters.
the manipulation consists of the following six motions.
1) Putting in counters.
(10)
2) Taking off counters.
3) Putting in five counter and taking off one-counter.
4) Putting in one-counter and taking off five counter.
5) Taking off counter of ones' place and putting in a
counter of tens place.
6) Taking off a counters of tens' place and putting in
counters of ones' place:
Note: In order to indicate 10, a counter in the lower
part on the next upright to the left is put in,
(11)
i.e. a counter in tens' place is put in.
In illustrating the manipulations which ar most
important in calculations, the following symbols are
used to facilitate one's understanding of its manipu-
lation.
^ Push up the counter with the thumb or fore
finger.
(In the case of taking off the counter in the
upper part, push up the counter with the
(12)
forefinger. (subtraction)
In the case of putting in the counter in the
lower part, push up the counter with the thumb.
(addition)
Push down the counter with the forefinger.
(means addition in the case of five counter)
(means subtraction in the case of one counter)
A counter already placed, i.e., a counter which
has already been "put in" and which remains
(13)
either on the top or at the bottom.
(*) A counter newly "put in".
(/) A counter "taken off".
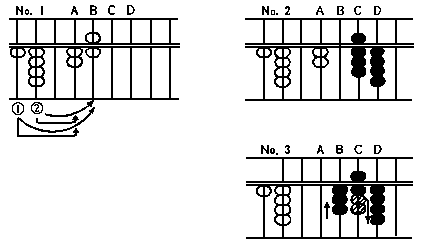
(A) 2 + 1
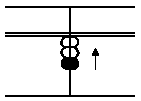 Answer: 3
In this case, first put in 2 with
the thumb, second, put in 1 with
thumb.
(14)
Answer: 3
In this case, first put in 2 with
the thumb, second, put in 1 with
thumb.
(14)
(B) 2 + 6
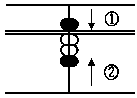 Answer: 8
In this case, put in 2 with the
thumb first.
Then put in 5 (upper part) with
the forefinger, and simultaneously
put in 1 (lower part) with the
thumb.
(15)
Answer: 8
In this case, put in 2 with the
thumb first.
Then put in 5 (upper part) with
the forefinger, and simultaneously
put in 1 (lower part) with the
thumb.
(15)
(C) 2 + 4
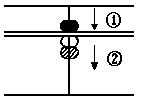 Answer: 6
First, put in 2 with the thu-
mb; Second, to add for put in
5 of the upper part and take
off 1, of the lower part with
the forefinger.
(16)
Answer: 6
First, put in 2 with the thu-
mb; Second, to add for put in
5 of the upper part and take
off 1, of the lower part with
the forefinger.
(16)
(D) 9 + 7
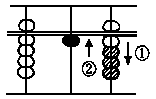 Answer: 16
First, put in 9 with the for-
efinger and thumb. Then to
add 7, take off 3 with the for-
efinger, and put in 1 in place
with the thumb, i.e., think 7
and 3 are 10. So take off 3 and
carry the 1 ten which is put in
the tens' the tens' place with thumb.
(17)
Answer: 16
First, put in 9 with the for-
efinger and thumb. Then to
add 7, take off 3 with the for-
efinger, and put in 1 in place
with the thumb, i.e., think 7
and 3 are 10. So take off 3 and
carry the 1 ten which is put in
the tens' the tens' place with thumb.
(17)
(E) 36 + 75
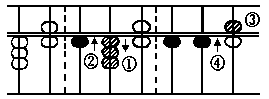 Answer: 111
To add two place
numbers and above,
always commence ad-
ding from the left to
the right.
In this case put in
7 tens i.e., add 7 tens of 75 to 3 tens of 36 in the
same method as in example D. Next add 5 ones to 6
ones in the following way.
(18)
Answer: 111
To add two place
numbers and above,
always commence ad-
ding from the left to
the right.
In this case put in
7 tens i.e., add 7 tens of 75 to 3 tens of 36 in the
same method as in example D. Next add 5 ones to 6
ones in the following way.
(18)
Take off 5 (a five counter) with the forefinger,
and simultaneously put in 1 ten in the tens' place
with the thumb as in example D.
[Other examples]
9 + 7 = 16 4 +27 = 31 3 + 8 = 11
7 + 5 = 12 23 +20 = 43 9 + 5 = 14
8 +13 = 21 2 + 8 = 10 21 + 8 = 29
50 +85 =135 6 + 9 = 15 76 +82 =158
6 + 7 = 13 31 + 7 = 38
8 + 6 = 14 25 +13 = 38
(19)
(F) 10 - 3
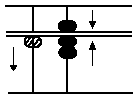 Answer: 7
In this case there are no ones.
Consequently 1 ten is borrowed
by taking off 1 ten with the
forefinger and 3 ones are subtra-
cted from it by putting in 7 ones,
the remainder, with the forefinger and thumb.
(20)
Answer: 7
In this case there are no ones.
Consequently 1 ten is borrowed
by taking off 1 ten with the
forefinger and 3 ones are subtra-
cted from it by putting in 7 ones,
the remainder, with the forefinger and thumb.
(20)
(G) 12 - 6
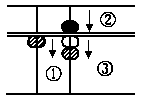 Answer: 6
In the same there are not enou-
gh) ones to subtract from. Cons-
equently, as in example (F) 1 ten
must be borrowed. With the
forefinger 1 ten is taken off and
the remainder 4 ones are put in
by putting in a five counter and taking off a one
counter in the ones' place.
(21)
Answer: 6
In the same there are not enou-
gh) ones to subtract from. Cons-
equently, as in example (F) 1 ten
must be borrowed. With the
forefinger 1 ten is taken off and
the remainder 4 ones are put in
by putting in a five counter and taking off a one
counter in the ones' place.
(21)
(H) 100 - 58
 Answer: 42
In subtraction involving
two place, three place num-
bers and above, always com-
mence from the left to the
right as in the case of addi-
tion. In this case subtract 5
tens of the number 58 from the tens. However, as
there are no tens, 1 hundred is borrowed in a same
manner as in example F. Next, in subtracting 8
(22)
Answer: 42
In subtraction involving
two place, three place num-
bers and above, always com-
mence from the left to the
right as in the case of addi-
tion. In this case subtract 5
tens of the number 58 from the tens. However, as
there are no tens, 1 hundred is borrowed in a same
manner as in example F. Next, in subtracting 8
(22)
ones, as there are no ones left, 1 ten must be
borrowed. 8 is subtracted and 2 ones, the remainder,
are put in by the same method as of example (F).
[Other examples]
4 - 2 = 2 5 - 3 = 2 6 - 2 = 4 8 - 6 = 2
17 - 4 =13 11 - 6 = 5 15 - 6 = 9 12 - 6 = 6
88 -45 =43 40 -15 =25 30 -22 = 8 27 -12 =15
136 -74 =62 112 -50 =62 300 -126=174 10000-41=959
Exercise for addition and subtraction.
(23)
"How to exercise?"
You need not care about the unit position.
(1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 First of all, put in
(2) 2 4 6 9 1 3 5 7 8 "123,456,789" on the
(3) 3 7 0 3 7 0 3 6 7 "Abacus", and then
(4) 4 9 3 8 2 7 1 5 6 put in "123,456,789"
(5) 6 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 5 eight times, i.e., and
(6) 7 4 0 7 4 0 7 3 4 "123,456,789" to "123,
(7) 8 6 4 1 9 7 5 2 1 456,789" eight times.
(8) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 1 2
----------------------
(9) 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
(24)
The sum is "1,111,101". This is exercise for addition.
For exercise of subtraction, subtract "123,456,
789" from "1,111,111,101 nine times. The
remainder "0".
Determination of unit position in the product:
1) In such case where the multiplier is the
integral or mixed decimal number (for example
3.56; 19.362 etc), count figures in the integral
(25)
part of the multiplier. Count off equal number
of uprights, from the unit position of the mult-
iplicand, toward the right: this upright is the
unit position for the product.
2) In case the multiplier is a decimal number (except
the mixed-decimal number) and there are
some 0's "Zeros" between the decimal point
and the decimal-significant figure 1, 2, 3, ......9:
Count a number of 0 "zero" between the decimal
(26)
point and the decimal-significant figure of the
multiplier. Count off an equal number of uprights,
from the unit position of the multiplcand,
toward the left: this upright is the unit position
for the product.
3) In such case where the multiplier is the decimal
number and there is no 0 "zero" between the
decimal point and the decimal-significant number
the unit position of the multiplicand is the unit
(27)
position for the product.
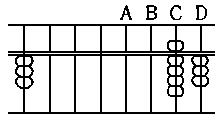
67 x 2 = 134
 14
12
---
134
Compare the last figure
of the multiplicand, i.e., 7
on the upright B, with the
multiplier 2. "2 x 7 is 14"
therefore, after taking off
7 from the upright B,
place 1, the first figure of
14, on the upright B, and
(28)
14
12
---
134
Compare the last figure
of the multiplicand, i.e., 7
on the upright B, with the
multiplier 2. "2 x 7 is 14"
therefore, after taking off
7 from the upright B,
place 1, the first figure of
14, on the upright B, and
(28)
Place 4, the second figure, on the upright C. Next,
compare 6, another figure in the multiplicand, with
the multiplier, 2.
"2 x 6 is 12" therefore, after taking off 6 from the
upright A, place 1, the first figure of 12, on the
upright A, then add2, the second figure, to 1 on
the upright B. The product is 134.
(29)
9 x 7 = 63
 63
Compare the multiplicand, i.
e., 8, with the multiplier 7. "9 x 7
is 63", ---therefore, take off
9 and place 6, the first figure
of 63, on the upright A, and
place 3, the second figure on
the upright. B, after taking off
9 from the upright A. The pro-
duct is 63
(30)
63
Compare the multiplicand, i.
e., 8, with the multiplier 7. "9 x 7
is 63", ---therefore, take off
9 and place 6, the first figure
of 63, on the upright A, and
place 3, the second figure on
the upright. B, after taking off
9 from the upright A. The pro-
duct is 63
(30)
26 x 14 = 364
 0 6
2 4
0 2
0 8
-------------
3 6 4
(31)
0 6
2 4
0 2
0 8
-------------
3 6 4
(31)
In illustration No. 1, we see that the multiplier is
a two place integral. Therefore, count off two
uprights, from the unit position of the multiplicand, i.
e., from the upright B, toward the right. The upright
D is the unit position for product.
Process of multiplication:
1) Compare the last figure of the multiplicand, i.
e., 6 on the upright B, with the first figure of
the multiplier i.e. 1.
(32)
"1 x 6 is 6" --- therefore, after taking off 6 from
the upright B, place 6 on the upright C.
2) Next, compare the same 6 with the second figure
of the multiplier. 4, "4 x 6 is 24" --- therefore, add
2, the first figure of 24, to 6 on the upright
C, and place 4, the second figure, on the upright
D.
3) Compare 2, the first figure of the multiplcand,
with 1, the first figure of the multiplier. "1 x 2"
(33)
is 2", therefore, place 2 on the upright B, after
taking off 2 from the upright A. Finally, compare
the same 2, the first figure of the multiplicand,
with 2, the second figure of the multiplier, "4 x 2
is 8" --- therefore add 8 to 8 on the upright C.
See illustration No. 3. The product is 364 as
shown on the "Abacus" now.
(34)
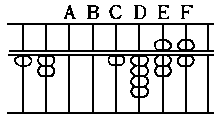
678 x 345 = 233910
 2 4 (1)
3 2 (2)
4 0 (3)
2 1 (4)
2 8 (5)
3 5 (6)
1 8 (7)
2 4 (8)
3 0 (9)
---------------
Required answer... 2 3 3 9 1 0
(35)
2 4 (1)
3 2 (2)
4 0 (3)
2 1 (4)
2 8 (5)
3 5 (6)
1 8 (7)
2 4 (8)
3 0 (9)
---------------
Required answer... 2 3 3 9 1 0
(35)
Determination of the unit ----------------------
position for the product: In multiplicand 394
this case, the multiplier is a ----------------------
three place integral, therefore, multiplier | product
count off three uprights, from ----------------------
the unit position of the mul- 2 |
tiplicand, i.e., from the up- 4 |
right C, toward the right: the 6 |
upright F is in the unit position 12 |
19 |
20 |
123 |
456 |
----------------------
(36)
for the product. The diagram above shows the diff-
erent steps on "Abacus" in the course of calculation
of "678 x 345". A B C D E F G
Note: The encircled ---------------
figures indicate the 4 0 7 6........multiplicand
steps in calculation. 1 2......(1) (2 x 6)
4.076 x 0.028 = 0.11428 4 8....(2) (8 x 6)
multiplier 1 4........(3) (2 x 7)
0.028 5 6......(4) (8 x 7)
8............(5) (2 x 4)
3 2..........(6) (8 x 4)
---------------
0 1 1 4 1 2 8
(37)
Note: The encircled figures indicate the steps in
calculation.
Determination of the unit position for the product:
In the above example, we see that the multiplier
has one 0 "zero" between the decimal point and the
decimal-significant figure. Therefore, count off one
upright from the unit position of the multiplicand, i.
e., from the upright B, towards the left: Then the
upright A is the unit position for the product.
(38)
Note: At first, calculate by placing both "multipli-
cand" and "multiplier" on the "Abacus". As
you practice on the "Abacus", calculate by
placing either the "multiplicand" or "multiplier"
on the "Abacus". If you practice further
and become proficient in calculation on the
"Abacus", calculation by placing neither of
them is possible. Calculation can be done more
rapidly this way.
(39)
Determination of the unit position for the quotient:
1) Count the figures in the integral part of the
divisor. Count off an equal number of uprights,
from the unit position of the dividend towards
the left: count off one more: and the upright is
the unit position for the quotient.
2) In such case as there are some 0's (zero's) between
the decimal point and the decimal-significant
(40)
figure of the divisor.
(A) Count the number of 0's ("zero"s) between the
decimal point an the decimal-significant
figure of the divisor. Count off an equal
number of upright, from the unit position of
the dividend towards the right: count off one
less: and the last upright is the unit position
for the quotient.
(B) In such case as there is one "0" ("zero")
(41)
between the decimal point and the decimal-
significant figure of the divisor, the unit
position of the dividend is the unit position
for the quotient.
3) In such case as there is no "0" ("zero") between
the decimal point and the decimal-significant
figure, next upright from the unit position of
the dividend towards
the left is the unit position for the quotient.
(42)
93 / 3 = 31
 divisor dividend
3 A B C D
9 3
3 9
---------
3 0 0 3
1 -3
---------
3 1
(43)
divisor dividend
3 A B C D
9 3
3 9
---------
3 0 0 3
1 -3
---------
3 1
(43)
In the above illustration, we see that the divisor
is a one-place integra therefore, count off one upright,
from the unit position of the dividend, i.e., from the
upright D, towards the left: count off one more: then
the last upright, i.e., the upright B is the unit
position for the quotient.
Process of division:
1) Compare the first figure of the dividend, i.e., 9
on the upright C, with the divisor 3. Find how
(44)
many 3's there are in 9 --- "9 / 3 is ?". There
are three 3's in 9, therefore, place 3 on the
upright A, as the quotient figure.
2) Multiply the divisor 3, by the quotient figure, 3
on the upright A. "3 x 3 is 9", therefore subtract
9 from the upright C.
3) Compare the remainder, 3 of the dividend on
the upright D, with the divisor 3. Find how
many 3's there are in 3, --- "3 / 3 is ?".
(45)
There is one 3 in 3, therefore, place on the
upright B as the quotient figure.
4) Multiply the divisor by the second quotient
figure of 1. "3 x 1 is 3" --- therefore, take off 3
from the upright D.
The quotient is 31.
(46)
1476 / 12 = 123
 divisor dividend
12 A B C D E F
1 4 7 6
1
-1
-2
---------------------
partial........2 7 6
dividend 2
-2
-4
---------------------
partial..........3 6
dividend 3
-3
-6
---------------------
quotient 1 2 3 0
(47)
divisor dividend
12 A B C D E F
1 4 7 6
1
-1
-2
---------------------
partial........2 7 6
dividend 2
-2
-4
---------------------
partial..........3 6
dividend 3
-3
-6
---------------------
quotient 1 2 3 0
(47)
In the left illustration, we see that the divisor is
a two-place integral; therefore, count off two uprig-
hts, from the unit position of the dividend, i.e., from
the upright F towards the left: count off one more;
then the last one the upright C, is the unit position
for the quotient.
Process of division:
1) Compare the first figure of the dividend, i.e., 1
on the upright C with the first figure of the
(48)
divisor of 12, i.e., 1. Find how many 1's there
are in 1 --- "1 / 1 is ?" There is one 1 in 1, there-
fore, place 1 on the upright A as the quotient
figure.
2) Multiply 1, the first figure of the divisor, by 1,
the first quotient figure on the upright A. "1 x 1
is 1" --- therefore, subtract 1 from the upright C.
3) Multiply 2, the second figure of the divisor, by 1,
the first quotient figure "1 x 2 is 2"; --- therefore,
(49)
subtract 2 from the upright D. Now you will get
276 which is the partial dividend.
4) Compare the first figure of the partial dividend
i.e., 2, with the first figure of the divisor of 12
i.e., 1. Find how many 1's there are in 2 ---
"2 / 1 is ?". There are two 1's in 2, therefore, place
2 on the upright B as the quotient figure.
5) Multiply 1, the first figure of the divisor by 2,
the second quotient figure on the upright B. "1
(50)
x 2 is 2" --- therefore, subtract 2 from the upri-
ght D.
6) Multiply 2, the second figure of the divisor, by
2, the second quotient figure. "2 x 2 is 4" ---
therefore, subtract 4 from the upright E. Now
you will get 36 as the partial dividend.
7) Compare the first figure of the partial dividend,
i.e., 3 with the first figure of the divisor of 12,
i.e., 1.
(51)
Find how many 1's there are in 3 --- "3 / 1 is ?".
There are three 1's in 3 therefore,
place 3 on the upright C as the quotient figure.
8) Multiply 1, the first figure of the divisor of 12, by
3, the last quotient figure on the upright C. "1
x 3 is 3" --- therefore, subtract 3 from the upri-
ght E.
9) Multiply 2, the second figure of the divisor by
3, the last quotient figure "2 x 3 is 6" -- therefore,
(52)
638 / 22 = 29 subtract 6 from the
divisor dividend upright F. The
22 A B C D E quotient is 123.
6 3 8 From the foregoing
3 explanations you can
6 see that the unit
-6 position for the quotient
----------- is the upright B.
3 0 0 3 8 1) Compare the first
-1 +2
-----------
2 0 2 3 8
-4
-----------
2 0 1 6 8
9
-1 8
-1 8
-----------
2 9
(53)
figure of the dividend, 6, with the figure of the
divisor 2.
Find how many 2's there are in 6, --- "6 / 2 is
?". There are three 2's in 6. Therefore, place 3 on
the upright A.
2) Multiply 2, the first figure of the divisor, by 3
the quotient figure on the upright A. "2 x 3 is 6"
--- therefore subtract 6 from the upright C.
3) Multiply 2, the second figure of divisor, by 3
(54)
the quotient figure "2 x 3 is 6" --- therefore, sub-
tract 6 from the upright D. But in this case, 6
cannot be subtracted from 3 on the upright D.
So, take 1 from 3, the quotient figure on the
upright A and replace 2, on the upright C (i.e.,
this 2, the first figure of divisor which had been
multiplied by 3. Then, multiply 2, the correct
quotient figure thus obtained on the upright A,
by 2, the second figure of divisor. "2 x 2 is 4" ---
(55)
therefore, subtract 4 from the upright D.
4) Divide 198, the partial dividend, by 22, the
divisor.
In this case, find how many 2's, the first figure
of the divisor, there are in 19, the first and
second figure of the partial dividend. "19 / 2 is ?".
There are nine 2's in 19. Therefore, place 9 on
the upright B as the last quotient figure.
5) Multiply 2, the first figure of the divisor, by 9,
(56)
the last quotient figure. "2 x 19 is 18" --- therefore,
subtract 18 from the upright C and D. Finally,
multiply 2, the second figure of the divisor, by 9
the last quotient figure "2 x 9 is 18" --- therefore,
subtract 18 from the upright D and E.
The quotient is 29.
-- E N D --
(57)
 Unit points on the crosspiece are usually placed
(7)
Unit points on the crosspiece are usually placed
(7)

Unit points on the crosspiece are usually placed (7)
Answer: 3 In this case, first put in 2 with the thumb, second, put in 1 with thumb. (14)
Answer: 8 In this case, put in 2 with the thumb first. Then put in 5 (upper part) with the forefinger, and simultaneously put in 1 (lower part) with the thumb. (15)
Answer: 6 First, put in 2 with the thu- mb; Second, to add for put in 5 of the upper part and take off 1, of the lower part with the forefinger. (16)
Answer: 16 First, put in 9 with the for- efinger and thumb. Then to add 7, take off 3 with the for- efinger, and put in 1 in place with the thumb, i.e., think 7 and 3 are 10. So take off 3 and carry the 1 ten which is put in the tens' the tens' place with thumb. (17)
Answer: 111 To add two place numbers and above, always commence ad- ding from the left to the right. In this case put in 7 tens i.e., add 7 tens of 75 to 3 tens of 36 in the same method as in example D. Next add 5 ones to 6 ones in the following way. (18)
Answer: 7 In this case there are no ones. Consequently 1 ten is borrowed by taking off 1 ten with the forefinger and 3 ones are subtra- cted from it by putting in 7 ones, the remainder, with the forefinger and thumb. (20)
Answer: 6 In the same there are not enou- gh) ones to subtract from. Cons- equently, as in example (F) 1 ten must be borrowed. With the forefinger 1 ten is taken off and the remainder 4 ones are put in by putting in a five counter and taking off a one counter in the ones' place. (21)
Answer: 42 In subtraction involving two place, three place num- bers and above, always com- mence from the left to the right as in the case of addi- tion. In this case subtract 5 tens of the number 58 from the tens. However, as there are no tens, 1 hundred is borrowed in a same manner as in example F. Next, in subtracting 8 (22)
14 12 --- 134 Compare the last figure of the multiplicand, i.e., 7 on the upright B, with the multiplier 2. "2 x 7 is 14" therefore, after taking off 7 from the upright B, place 1, the first figure of 14, on the upright B, and (28)
63 Compare the multiplicand, i. e., 8, with the multiplier 7. "9 x 7 is 63", ---therefore, take off 9 and place 6, the first figure of 63, on the upright A, and place 3, the second figure on the upright. B, after taking off 9 from the upright A. The pro- duct is 63 (30)
0 6 2 4 0 2 0 8 ------------- 3 6 4 (31)
2 4 (1) 3 2 (2) 4 0 (3) 2 1 (4) 2 8 (5) 3 5 (6) 1 8 (7) 2 4 (8) 3 0 (9) --------------- Required answer... 2 3 3 9 1 0 (35)
 divisor dividend
3 A B C D
9 3
3 9
---------
3 0 0 3
1 -3
---------
3 1
(43)
divisor dividend
3 A B C D
9 3
3 9
---------
3 0 0 3
1 -3
---------
3 1
(43)
divisor dividend 12 A B C D E F 1 4 7 6 1 -1 -2 --------------------- partial........2 7 6 dividend 2 -2 -4 --------------------- partial..........3 6 dividend 3 -3 -6 --------------------- quotient 1 2 3 0 (47)